经常有人问,闲来无事写个教程。
什么是端口转发?为什么要转发?
准确来讲叫流量转发,因为流量是基于端口的,所以一般称为端口转发。
比如电信到伯力很差,我买了个上海联通鸡做转发,那么就是
电信->联通:1200->伯力:4900,那么我访问联通的1200端口,等于访问伯力的4900端口
转发还可以用于公网frp,反代网站等用途
用什么转发?
推荐iptables或者firewalld,都是内核级别的转发,性能损耗极少。
如果用gost/brook等第三方工具转发,流量大或者连接数过多的时候cpu和负载压力变大,对于nat小鸡特别不友好。
正文开始
基于firewalld转发(适用于centos7)
我记得debian也能安装firewalld,能安装的话一样可以用他来转发。
以下命令都在中转机(上海联通)执行
先停止iptables
systemctl stop iptables
systemctl disable iptables
安装,开机启动
yum install firewalld
systemctl start firewalld
systemctl enable firewalld.service
状态:显示绿色active说明服务运行正常
systemctl status firewalld
开启内核转发,然后重启
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
sysctl -p
reboot
到这里安装完成,
然后直接编辑vi /etc/firewalld/zones/public.xml文件,这个是firewalld配置文件
把下面的配置粘贴进去
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<zone>
<short>Public</short>
<description>For use in public areas. You do not trust the other computers on networks to not harm your computer. Only selected incoming connections are accepted.</description>
<service name="ssh"/>
<service name="dhcpv6-client"/>
<port protocol="tcp" port="10-65000"/>
<port protocol="udp" port="10-65000"/>
<masquerade/>
<forward-port to-addr="远程ip" to-port="远程端口" protocol="tcp" port="本地端口"/>
<forward-port to-addr="远程ip" to-port="远程端口" protocol="udp" port="本地端口"/>
</zone>
重启防火墙就生效了
systemctl restart firewalld.service
是不是比百度出来的一大堆命令要简单,
每次修改 public.xml 要重启防火墙才会生效
用站长工具扫描一下上海联通ip的1200端口,开了说明转发成功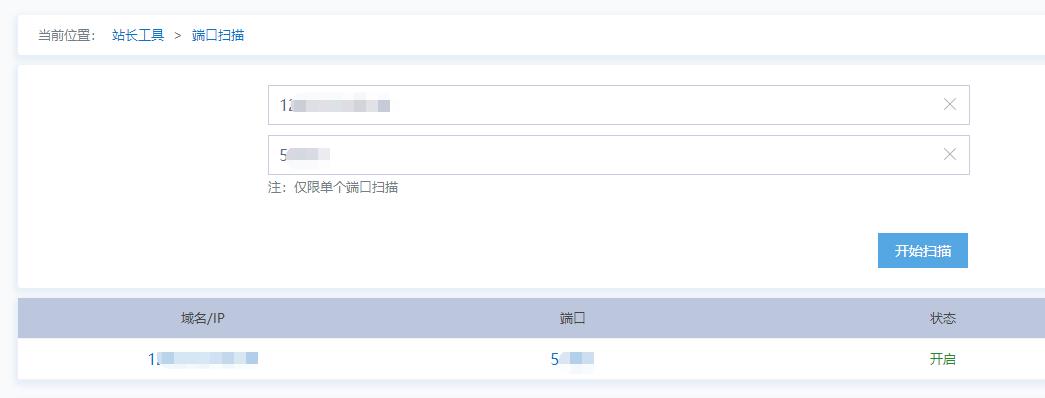
此时访问 海联通ip:1200端口,等于访问伯力:4900端口
也就是把你的v2 sr的客户端,ip和端口改为 海联通ip和1200,就可以了!
基于iptables转发(适用于C7,D8)
先安装iptables,debian换成 apt-get install
yum install -y iptables
yum install -y iptables-services
开机启动
systemctl start iptables
systemctl enable iptables
查看服务状态,显示绿色active就可以了
service iptables status
清空所有防火墙规则,避免因端口没开造成影响
iptables -F
iptables -X
开启内核转发,重启
echo -e "net.ipv4.ip_forward=1" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
sysctl -p
reboot
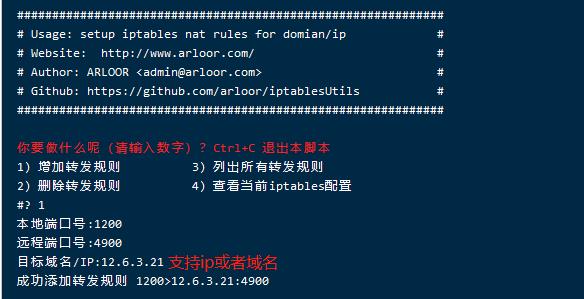
到这里安装完成,然后用知名的转发脚本,按提示转发。
这个脚本是帮你一键执行iptables命令,还是调用iptables,非第三方转发软件,支持ddns,感谢arloor
https://github.com/arloor/iptablesUtils
wget --no-check-certificate -qO natcfg.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/arloor/iptablesUtils/master/natcfg.sh && bash natcfg.sh